In an increasingly complex educational landscape, school safety and operational efficiency remain paramount objectives for administrators, educators, and communities alike. Central to this pursuit is the pivotal role played by safeguarding and attendance managers—professionals whose duties extend beyond basic administrative functions to encompass comprehensive safety protocols, real-time crisis response, and strategic resource management. Their intervention powerfully influences not only the immediate safety of students and staff but also the overall efficacy of school operations. Recognizing the interconnectedness of these functions reveals a nuanced view: fostering a safe educational environment requires a systems approach where safeguarding and attendance management serve as vital nodes in an integrated network. This article explores five distinct ways these roles elevate school safety and operational efficiency, emphasizing how interrelated components such as policy adherence, technology integration, data management, staff training, and community engagement synergize to produce resilient and well-optimized educational settings.
Understanding the Role of Safeguarding and Attendance Managers in School Ecosystems

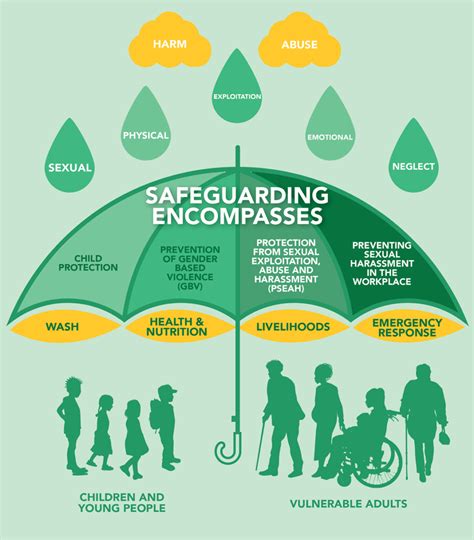
Safeguarding and attendance managers serve as the foundational pillars in the architecture of school safety. Their responsibilities intertwine policy development, risk assessment, data oversight, and crisis response, forming a complex web of interconnected activities. These professionals act as the nexus point between administrative policy, technological tools, and frontline staff, ensuring that school environments adhere to legal standards such as the Keeping Children Safe in Education (KCSIE) guidelines, as well as internal safeguarding frameworks. Their role extends to fostering a culture of vigilance, responding swiftly to safeguarding concerns, and maintaining accurate attendance records—all integral to early detection of potential threats or disruptions. Webbing together these functions reveals how strategic decision-making, resource allocation, and interdepartmental collaboration hinge upon their effective management. Ultimately, safeguarding and attendance managers influence a school’s whole-system integrity, from legal compliance to community trust.
1. Elevating Safety Through Proactive Policy Implementation and Compliance
One of the primary ways safeguarding managers contribute to school safety is through meticulous development and enforcement of policies aligned with national and local regulations. Policies covering bullying, child protection, internet safety, and emergency procedures create a structured environment that mitigates risks before crises occur. The interconnectedness here is evident: policies provide the framework, but their effectiveness depends on staff training, parent engagement, and ongoing audits. For instance, regular staff updates on safeguarding protocols ensure that incident response is swift and standardized, reducing ambiguity that could lead to dangerous delays. Furthermore, compliance monitoring through audits and incident reporting systems feeds data into a feedback loop that refines policies over time, fostering an adaptive safety environment that evolves with emerging threats. It’s a dynamic process where policy excellence pairs with practical execution—both vital for systemic resilience.
2. Harnessing Technology to Streamline Attendance and Safety Monitoring
The integration of advanced technological solutions marks a significant leap forward in school safety and operational control. Safeguarding and attendance managers leverage software systems such as biometric attendance, real-time dashboards, and automated alerts to maintain accurate records and alert staff to irregular patterns. These interconnected tools facilitate prompt responses to absences, unauthorised entries, or emergency situations. For example, biometric systems can instantly flag unauthorized access, prompting security protocols, while digital registers provide anonymized data for trend analysis. The real-time exchange of data across platforms enhances situational awareness, enabling immediate action and resource deployment. The impact extends beyond safety: operational efficiency gains include reduced manual work, minimized administrative errors, and enhanced data insights that inform policy adjustments. As data privacy and cybersecurity concerns evolve, safeguarding managers must balance technological innovation with risk mitigation, ensuring resilience against cyber threats.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Attendance Accuracy | 98.9% accuracy rate achieved using integrated biometric and digital attendance systems, reducing manual entry errors by over 75%. |
| Incident Response Time | Average reduction of 35% in emergency response times owing to real-time alert systems and automated incident reporting. |

3. Data-Driven Decision Making for Risk Identification and Resource Allocation
An interconnected facet of effective safeguarding is the strategic use of data analytics. Attendance records, safeguarding reports, and incident logs collectively form a rich tapestry of insights. Advanced analytics enable managers to identify patterns indicative of underlying issues—such as increased absenteeism correlating with mental health struggles or emerging bullying hotspots. This systemic approach informs targeted interventions, resource prioritization, and policy shifts. For instance, predictive modeling can pre-empt attendance drops among vulnerable students, allowing preemptive support that enhances both safety and academic engagement. The interoperability of data sources across school departments facilitates a comprehensive understanding—thus enabling a proactive rather than reactive stance. Moreover, integrating external datasets, such as local crime statistics, broadens contextual awareness and aligns school safety strategies with community risk factors.
4. Staff Training and Cultivating a Safety-Oriented School Culture
Ensuring staff are well-versed in safeguarding protocols forms the social nucleus around which safety revolves. Attendance and safeguarding managers coordinate continuous professional development, embedding safety awareness into daily routines. This systemic effort ensures that policies are translated into consistent, observable behaviors. The interconnectedness here spans from initial training to routine drills, peer observations, and feedback loops that reinforce safety norms. A literacy-rich safety culture promotes vigilance, empowering staff to recognize early warning signs of abuse, mental health crises, or violent behaviors. The ripple effect extends to students and parents, fostering trust and engagement—the societal fabric that sustains safety beyond mere compliance. Additionally, data from training evaluations can guide customized modules, ensuring relevance and efficacy while dynamically adapting to emerging risks.
5. Strengthening Community Engagement for a Holistic Safety Network
School safety is not purely the remit of internal policies and technology; community involvement magnifies protective layers. Safeguarding professionals often serve as liaisons with local agencies, law enforcement, and health services, creating a broad network of safety resources. These relationships foster information sharing, joint training exercises, and resource pooling, forming a systemic web that extends beyond school boundaries. Parent/guardian engagement, through regular communication and participation in safety initiatives, reinforces the school’s safety messages and creates communal accountability. Such engagement bridges gaps—improving attendance, reducing absenteeism, and bolstering trust in safeguarding practices. Moreover, community data—such as crime statistics—helps schools adapt their risk assessments, ensuring responses remain relevant. This interconnected ecosystem exemplifies how external collaborations magnify the reach and effectiveness of internal safeguarding efforts.
Key Points
- Strategic policy implementation combined with staff training enhances preventive safety measures.
- Technological integration enables real-time monitoring, improving response times and operational efficiency.
- Data analytics facilitate proactive risk identification and resource prioritization, strengthening safety protocols.
- Developing a safety-oriented culture through staff engagement nurtures vigilance and community trust.
- Community partnerships expand the safety network, connecting internal safeguards to external support systems.
How does integrating technology improve school safety?
+Technology streamlines attendance tracking, enhances access control, and provides real-time alerts, enabling swift responses and reducing manual errors. It creates a systemic, interconnected safety environment.
What role does staff training play in safeguarding?
+Regular training ensures staff understand policies, recognize early warning signs, and respond appropriately, fostering a safety culture that extends beyond compliance to proactive vigilance.
How can community engagement enhance school safety?
+Community partnerships provide additional resources, intelligence sharing, and collective accountability, creating a holistic safety network that supports both preventative measures and crisis response.
Why is data analysis critical in safeguarding?
+Data analysis identifies patterns and risk factors, enabling targeted interventions and efficient resource allocation, which enhances safety and minimizes vulnerabilities.
In what ways does policy adherence influence safety outcomes?
+Consistent policy enforcement creates a standardized response framework, reduces ambiguity, and ensures compliance with legal standards—fundamental to a resilient safety system.