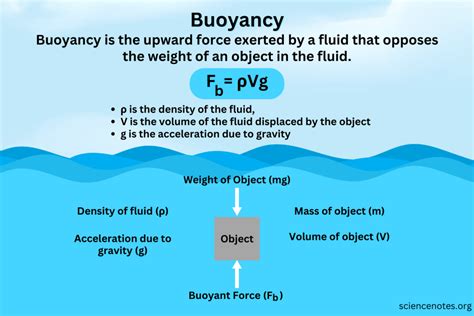
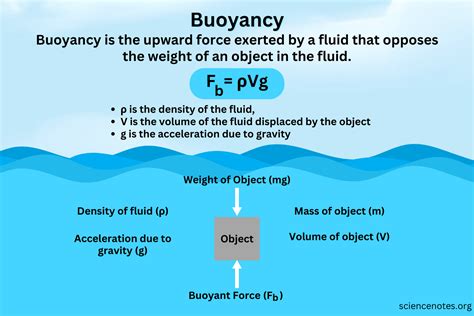
The concept of buoyant force is a fundamental principle in physics, particularly in the field of fluid mechanics. It is the upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of an object immersed in it. The buoyant force formula is a crucial tool for calculating this force and understanding its implications in various engineering and scientific applications.
Understanding the Buoyant Force

The buoyant force is a result of the difference in pressure between the top and bottom of an object when it is partially or fully submerged in a fluid. According to Archimedes’ Principle, the buoyant force on an object is equal to the weight of the fluid it displaces. This principle is widely used in the design of ships, submarines, and other watercraft, as well as in the analysis of the stability of these vessels.
Derivation of the Buoyant Force Formula
The buoyant force formula can be derived from the definition of the buoyant force as the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. If an object of volume V is submerged in a fluid of density ρ, the weight of the fluid displaced is given by the product of the volume of the displaced fluid, the density of the fluid, and the acceleration due to gravity g. Therefore, the buoyant force F_b can be expressed as:
F_b = ρVg
This formula shows that the buoyant force is directly proportional to the density of the fluid, the volume of the displaced fluid, and the acceleration due to gravity.
| Variable | Description | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| F_b | Buoyant force | N (Newtons) |
| ρ | Density of the fluid | kg/m³ |
| V | Volume of the displaced fluid | m³ |
| g | Acceleration due to gravity | m/s² |
Applications of the Buoyant Force Formula

The buoyant force formula has numerous applications in various fields, including engineering, physics, and oceanography. Some of the key applications include:
- Ship design: The buoyant force formula is used to calculate the buoyancy of ships and ensure their stability in different sea conditions.
- Submarine design: The formula is used to calculate the buoyancy of submarines and control their depth and stability underwater.
- Offshore structure design: The buoyant force formula is used to calculate the buoyancy of offshore structures, such as oil rigs and wind turbines, and ensure their stability in harsh marine environments.
- Underwater vehicle design: The formula is used to calculate the buoyancy of underwater vehicles, such as remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) and autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs), and control their depth and stability.
Key Points
- The buoyant force formula is F_b = ρVg, where F_b is the buoyant force, ρ is the density of the fluid, V is the volume of the displaced fluid, and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
- The formula is derived from Archimedes' Principle, which states that the buoyant force on an object is equal to the weight of the fluid it displaces.
- The buoyant force is directly proportional to the density of the fluid, the volume of the displaced fluid, and the acceleration due to gravity.
- The formula has significant implications in engineering design, particularly in the development of offshore structures, pipelines, and underwater vehicles.
- The buoyant force formula is used to calculate the buoyancy of ships, submarines, offshore structures, and underwater vehicles, and ensure their stability in different environments.
Limitations and Considerations
While the buoyant force formula is a powerful tool for calculating the buoyancy of objects in fluids, there are several limitations and considerations that must be taken into account. These include:
- Fluid density variations: The density of the fluid can vary with temperature, pressure, and other factors, which can affect the accuracy of the buoyant force calculation.
- Object shape and size: The shape and size of the object can affect the volume of the displaced fluid and the resulting buoyant force.
- Fluid viscosity: The viscosity of the fluid can affect the flow of the fluid around the object and the resulting buoyant force.
By understanding these limitations and considerations, engineers and scientists can use the buoyant force formula to make more accurate calculations and design more efficient and stable structures and vehicles.
What is the buoyant force formula?
+The buoyant force formula is F_b = ρVg, where F_b is the buoyant force, ρ is the density of the fluid, V is the volume of the displaced fluid, and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
What are the applications of the buoyant force formula?
+The buoyant force formula has numerous applications in various fields, including engineering, physics, and oceanography. Some of the key applications include ship design, submarine design, offshore structure design, and underwater vehicle design.
What are the limitations and considerations of the buoyant force formula?
+While the buoyant force formula is a powerful tool for calculating the buoyancy of objects in fluids, there are several limitations and considerations that must be taken into account. These include fluid density variations, object shape and size, and fluid viscosity.