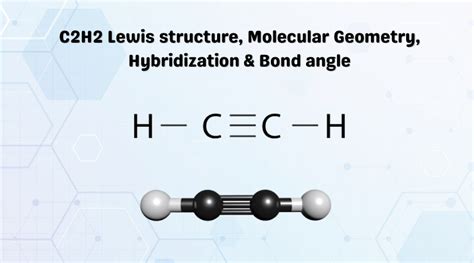
The C2H2 Lewis structure, also known as the acetylene molecule, is a fundamental concept in organic chemistry. To understand the Lewis structure, we must first grasp the basic principles of Lewis theory, which involves the representation of molecules using dots and lines to symbolize electrons and bonds, respectively. The C2H2 molecule consists of two carbon atoms (C) and two hydrogen atoms (H), with each carbon atom bonded to the other and each hydrogen atom bonded to one of the carbon atoms.
Understanding the Lewis Structure Basics
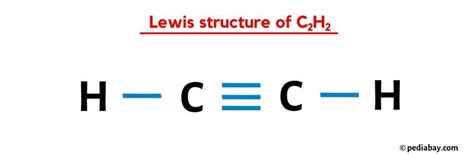
According to Lewis theory, atoms tend to achieve a stable noble gas configuration by forming bonds, which involves sharing pairs of electrons. Carbon has six valence electrons and needs four more to achieve the noble gas configuration of neon. Hydrogen, on the other hand, has one valence electron and needs one more to achieve the noble gas configuration of helium. The C2H2 molecule is formed when two carbon atoms share three pairs of electrons (a triple bond) and each carbon atom shares one pair of electrons with a hydrogen atom (a single bond).
Drawing the C2H2 Lewis Structure
To draw the Lewis structure of C2H2, we start by placing the atoms relative to each other. The two carbon atoms are placed in the center, and the hydrogen atoms are placed on either side, each bonded to one of the carbon atoms. Next, we distribute the valence electrons around the atoms. Each carbon atom has four valence electrons, and each hydrogen atom has one. We then form bonds between the atoms by sharing electron pairs. The carbon atoms form a triple bond (one sigma bond and two pi bonds), and each carbon atom forms a single bond with a hydrogen atom.
| Atom | Valence Electrons | Bonds Formed |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | 4 | Triple bond with C, single bond with H |
| Hydrogen (H) | 1 | Single bond with C |
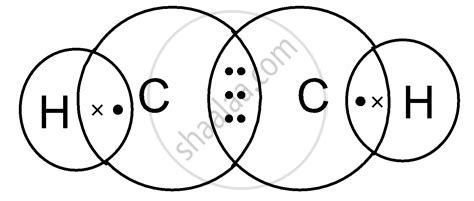
Key Points About the C2H2 Lewis Structure
Key Points
- The C2H2 molecule consists of two carbon atoms and two hydrogen atoms.
- The carbon atoms form a triple bond, and each carbon atom forms a single bond with a hydrogen atom.
- The Lewis structure is a two-dimensional representation of the molecule and does not reflect its actual shape or geometry.
- The C2H2 molecule has a linear geometry due to the triple bond between the carbon atoms.
- Understanding the Lewis structure is crucial for predicting the chemical properties and reactivity of the molecule.
Implications of the C2H2 Lewis Structure
The C2H2 Lewis structure has significant implications for the chemical properties and reactivity of the molecule. The triple bond between the carbon atoms makes the molecule highly reactive, particularly towards addition reactions. The linear geometry of the molecule also influences its physical properties, such as its boiling point and melting point. Understanding the Lewis structure of C2H2 is essential for predicting its chemical behavior and for designing chemical reactions that involve this molecule.
In conclusion, the C2H2 Lewis structure is a fundamental concept in organic chemistry that provides valuable insights into the chemical properties and reactivity of the acetylene molecule. By understanding the Lewis structure, chemists can predict the molecule's behavior and design chemical reactions that involve this molecule. The C2H2 Lewis structure is an excellent example of how Lewis theory can be applied to understand the chemical properties of molecules and to predict their reactivity.
What is the significance of the triple bond in the C2H2 Lewis structure?
+The triple bond in the C2H2 Lewis structure makes the molecule highly reactive, particularly towards addition reactions. The triple bond is a key factor in determining the chemical properties and reactivity of the molecule.
How does the linear geometry of the C2H2 molecule influence its physical properties?
+The linear geometry of the C2H2 molecule influences its physical properties, such as its boiling point and melting point. The linear shape of the molecule allows for stronger intermolecular forces, which affects its physical properties.
What is the importance of understanding the Lewis structure of C2H2?
+Understanding the Lewis structure of C2H2 is essential for predicting its chemical properties and reactivity. The Lewis structure provides valuable insights into the molecule’s behavior and allows chemists to design chemical reactions that involve this molecule.