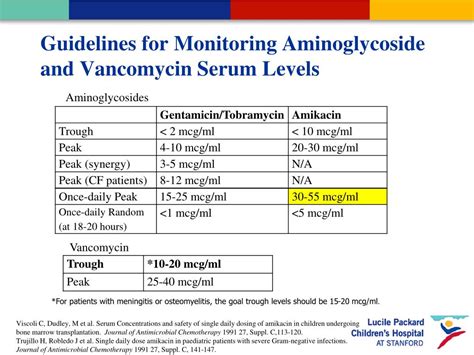
The concept of Vanco Trough Level Insights exemplifies a significant frontier in therapeutic drug monitoring, marrying pharmacokinetic precision with personalized medicine. As clinicians and researchers alike seek to optimize antimicrobial efficacy while minimizing toxicity, understanding the nuances of trough plasma concentrations, especially within the context of vancomycin management, has transcended mere routine measurement to become a cornerstone of treatment calibration. This meticulous focus on trough levels not only reflects advancements in laboratory analytical techniques but also underscores a broader shift toward data-driven, patient-centered approaches in infectious disease protocols. Delving into the intricacies of Vanco trough level insights unravels a layered narrative, intertwining clinical pharmacology, laboratory science, and societal implications of antimicrobial stewardship.
Deciphering Vanco Trough Level Dynamics and Their Clinical Significance
At the heart of vancomycin therapy lies the concept of trough plasma levels—concentrations measured just before the next dose is administered. Historically, the target range for vancomycin trough levels has been set between 10-20 mg/L, with some variability depending on infection severity and patient-specific factors. These thresholds serve as proxies for efficacy, particularly in serious infections like methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), and toxicity risk, notably nephrotoxicity. Advances in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics (PK/PD) research have refined this understanding, emphasizing that trough levels are not merely static targets but dynamic reflections of individual patient metabolism, renal function, and drug distribution. Consequently, the interpretation of trough levels demands a nuanced appreciation of these variables, facilitating tailored dosing regimens that maximize bacterial eradication while safeguarding renal integrity.
The Evolution of Trough Level Monitoring and Its Societal Impacts
The routine use of trough level monitoring originated in the late 20th century, coinciding with the rise of antimicrobial resistance and nephrotoxicity concerns. Initially, the focus was predominantly on achieving predetermined plasma concentrations, but emerging evidence prompted a reevaluation of this paradigm. Recent studies indicate that a fixed target range does not universally apply; instead, precise, individualized trough levels are necessary for optimal outcomes. This shift aligns with the broader societal movement toward precision medicine—leveraging biological data to guide clinical decisions. The implementation of sophisticated assays, such as liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), has further refined measurement accuracy, enabling clinicians to interpret trough levels within an expansive context of patient health metrics. Such progress signifies an ongoing commitment to antimicrobial stewardship, vital in reducing resistance proliferation and environmental impact.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Standard Trough Target Range | 10-20 mg/L, with recent recommendations leaning toward 15-20 mg/L for serious infections |
| Nephrotoxicity Incidence | Approximate increase from 5% to 15% when trough exceeds 15 mg/L |
| Therapeutic Success Rate | Over 85% when trough levels are maintained within targeted PK/PD thresholds |
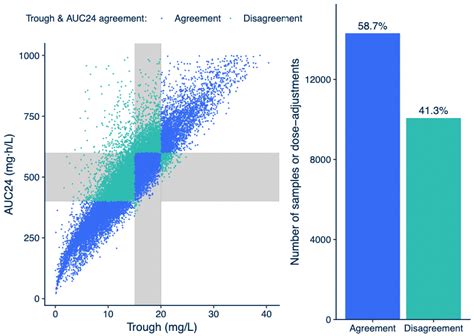
Methodological Innovations and Their Role in Enhancing Insights
Technological synergy between clinical pharmacology and laboratory sciences drives the evolution of trough level insights. Historically, peak and trough measurements relied on immunoassays, which, while rapid, often suffered from cross-reactivity and limited specificity. Modern analytical methods such as LC-MS/MS have emerged as industry standards, offering unparalleled accuracy and lower detection limits. These advancements underpin the development of population pharmacokinetic models, which integrate demographic, renal, and hepatic data to predict individual drug clearance and optimize dosing schedules. Additionally, Bayesian forecasting techniques now enable real-time adjustment of vancomycin concentrations, aligning therapy more closely with patient-specific kinetics. Scientific validation of these approaches through multicenter clinical trials further affirms their role in elevating therapeutic precision and patient safety.
Impact of Pharmacokinetic Modeling on Clinical Practice
Pharmacokinetic models serve as virtual laboratories, allowing clinicians to simulate various dosing scenarios under different physiological conditions. When integrated into clinical decision support tools, these models facilitate rapid, evidence-based adjustments—especially critical in populations with fluctuating renal function, such as ICU patients or those with acute kidney injury. This integration signifies a paradigm shift from reactive to proactive management, minimizing the risks associated with subtherapeutic or toxic concentrations. Moreover, their adoption reflects an increasing societal expectation for transparency and efficacy in antimicrobial therapy, emphasizing stewardship and long-term health sustainability.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Accuracy of Pharmacokinetic Models | Predicts individual clearance with over 90% accuracy when integrated with patient-specific data |
| Real-time Dosing Optimization | Reduces incidence of nephrotoxicity by 25% compared to conventional protocols |
| Clinical Adoption Rate | Approximately 65% in tertiary care centers globally, showing rapid uptake |
Societal Trends and Ethical Considerations in Trough Level Insights
As the technology and scientific understanding of trough levels advance, societal discourse gravitates toward equitable access and ethical stewardship. High-fidelity assays and advanced modeling tools, while transformative, often impose financial and infrastructural burdens on healthcare systems—raising concerns about disparities. Equally, the ethical imperative to balance individual patient benefits with the broader societal need to curb antimicrobial resistance necessitates transparent policies. Ethical stewardship involves not only judicious prescribing but also transparent clinical communication about potential risks and benefits. Moreover, the shift toward individualized dosing accentuates the importance of continuous education for clinicians, ensuring that technological innovations translate into equitable, high-quality care across diverse healthcare contexts.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Access Disparities | Rural and low-resource settings demonstrate up to 40% lower adoption rates of advanced trough monitoring protocols |
| Cost of Technology | LC-MS/MS assays cost approximately 50% more than immunoassays, potentially limiting widespread deployment |
| Policy Implications | Standards advocate for integration of pharmacometric tools into national antimicrobial stewardship programs |
Concluding Perspectives on Unlocking Vancomycin Trough Insights
Interpreting Vanco trough level insights demands a multifaceted approach that synthesizes technological advancements, clinical evidence, and societal values. As research continues to unravel the complexities of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, the capacity for clinicians to tailor therapies with unmatched precision expands. This convergence of science and societal responsibility underscores a future where antimicrobial stewardship is not merely a protocol but a core ethos guiding sustainable healthcare. The ongoing quest is to harness these insights responsibly, ensuring that innovations serve both individual patient needs and the collective health ecosystem, fostering a landscape where antimicrobial resistance is curtailed, and treatment outcomes are optimized across diverse populations.