The command shutdown is a crucial function in the world of computing, allowing users to safely power off their systems. While seemingly straightforward, this command holds significant importance in maintaining the integrity of data and hardware. In this comprehensive article, we delve into the intricacies of the shutdown command, exploring its various aspects, practical applications, and the potential risks and benefits it presents.
Understanding the Shutdown Command
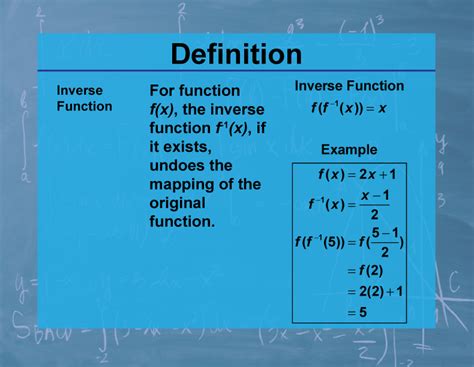
At its core, the shutdown command is a tool designed to gracefully terminate a computer’s operations, ensuring all ongoing processes are properly closed and data is saved before the system powers down. This command is particularly vital for preventing data loss and potential hardware damage, especially when compared to abrupt power interruptions.
The shutdown command is a versatile tool, offering a range of options to suit different scenarios. It can be used to immediately power off the system, schedule a shutdown for a specific time, or even force a shutdown if the system is unresponsive. This flexibility makes it an indispensable asset for system administrators and everyday users alike.
Technical Specifications
From a technical standpoint, the shutdown command is typically executed via the command-line interface (CLI) or through graphical user interfaces (GUIs) provided by operating systems. In the CLI, the command is invoked with the shutdown keyword followed by various options and parameters. These options can include specifying a delay time, providing a shutdown message, or forcing a shutdown without user confirmation.
For instance, the command shutdown -h 30 "System shutdown in 30 minutes" will initiate a system shutdown in 30 minutes, displaying the specified message to all logged-in users. Similarly, the command shutdown -r now will restart the system immediately.
| Command Option | Description |
|---|---|
| -h | Specifies the time in seconds before the system is powered off. |
| -r | Initiates a system restart. |
| -p | Powers off the system without shutting it down first. |
| -a | Cancels a pending shutdown. |
Practical Applications and Benefits
The shutdown command finds utility in numerous scenarios. For system administrators, it is an essential tool for managing server farms, ensuring that updates and maintenance can be performed without disrupting operations. It is also invaluable for remote system management, allowing administrators to initiate controlled shutdowns even when they are not physically present.
For everyday users, the shutdown command provides a simple and effective way to safely power off their systems, especially when combined with automation tools. This can be particularly useful for setting up scheduled shutdowns during periods of inactivity, helping to conserve energy and extend hardware lifespan.
Case Study: Server Maintenance
Consider a scenario where a system administrator needs to perform maintenance on a server farm. By using the shutdown command with the -h option, they can schedule a shutdown for a specific time, ensuring that all servers are powered off before maintenance begins. This controlled shutdown process minimizes the risk of data loss and hardware damage, making it an essential step in server management.
Furthermore, the shutdown command can be integrated with monitoring tools to automatically shut down servers when certain conditions are met. For example, if a server's CPU usage exceeds a certain threshold for an extended period, the monitoring tool can trigger a shutdown to prevent overheating and potential hardware failure.
Potential Risks and Mitigation Strategies
While the shutdown command is generally a safe and reliable tool, there are potential risks associated with its use. One of the primary concerns is the possibility of data loss if the shutdown is not properly executed. This can occur if the system is unstable or if a critical process is interrupted during the shutdown sequence.
To mitigate these risks, it is crucial to ensure that the system is in a stable state before initiating a shutdown. This can involve saving all open files, closing unnecessary applications, and ensuring that all critical processes are properly terminated. Additionally, it is good practice to have a backup strategy in place to recover data in case of unexpected shutdowns or system failures.
Future Implications and Innovations
As technology advances, the shutdown command is likely to evolve to meet new challenges and requirements. One potential development is the integration of machine learning algorithms to optimize shutdown processes. These algorithms could analyze system behavior and adapt the shutdown sequence to ensure the most efficient and reliable power-down.
Additionally, with the increasing adoption of cloud computing and virtualization, the shutdown command may need to adapt to work seamlessly in these environments. This could involve developing new command options or tools specifically designed for cloud-based systems, ensuring that shutdowns can be performed efficiently and securely across multiple virtual machines.
The Role of Automation
Automation is set to play a significant role in the future of shutdown processes. By automating shutdown procedures, system administrators can reduce the risk of human error and ensure consistent, reliable shutdowns. This can be particularly beneficial in large-scale environments, where managing multiple systems can be complex and time-consuming.
For example, an automated shutdown process could involve monitoring system performance, identifying optimal shutdown times based on usage patterns, and then executing the shutdown sequence without manual intervention. This level of automation could greatly enhance system reliability and efficiency, especially in dynamic computing environments.
Conclusion
The shutdown command is a fundamental tool in the realm of computing, offering a controlled and safe method for powering off systems. Its versatility and reliability make it an essential asset for both system administrators and everyday users. By understanding its technical specifications, practical applications, and potential risks, users can leverage this command effectively and efficiently.
As technology continues to advance, the shutdown command is likely to evolve, adapting to new computing paradigms and requirements. With its integration into automation and machine learning, the shutdown process is set to become even more efficient and reliable, ensuring the continued integrity of data and hardware.
Frequently Asked Questions
What happens if I force a shutdown without saving my work?
+Forcing a shutdown without saving your work can lead to data loss. It is always recommended to save your work before initiating a shutdown, especially if you are using the force option. Unsaved data may be lost, and recovery can be difficult or impossible.
Can I schedule a shutdown for a specific date and time?
+Yes, you can schedule a shutdown for a specific date and time using the shutdown command with the -s option followed by the desired time and date. For example, shutdown -s 2023-09-05 18:00 will schedule a shutdown for September 5th, 2023, at 6:00 PM.
Is it safe to force a shutdown if my system is unresponsive?
+Forcing a shutdown should only be used as a last resort when your system is completely unresponsive. While it can help resolve certain issues, it may also result in data loss or corruption. It is always recommended to try other methods first, such as using the Task Manager or restarting the system normally.
How can I monitor the progress of a scheduled shutdown?
+You can monitor the progress of a scheduled shutdown by using the shutdown -a command. This will display the remaining time until the scheduled shutdown. Additionally, some operating systems provide visual indicators or notifications to inform users of an upcoming shutdown.