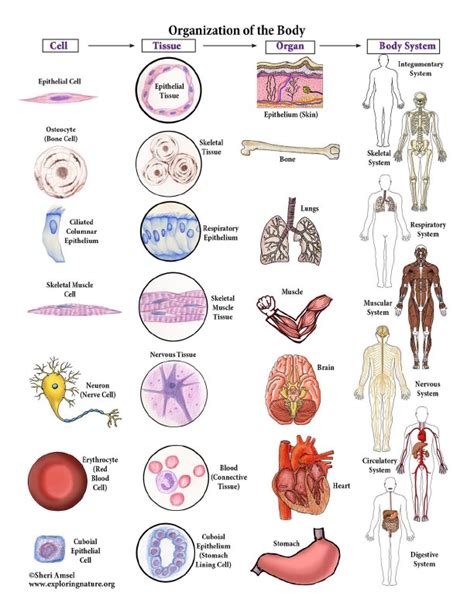
The human body is a complex and fascinating entity, comprising various organ systems that work in tandem to maintain overall health and function. At the core of these systems are cells, the fundamental building blocks of life. Understanding the intricacies of organ systems and their cellular composition is essential for appreciating the remarkable machinery that is the human body. In this article, we will delve into the world of organ systems and cells, exploring their structure, function, and interdependencies.
Key Points
- The human body is composed of 11 major organ systems, each with unique cellular characteristics and functions.
- Cells are the basic units of life, and their specialization and organization give rise to the diverse range of tissues and organs.
- The integumentary system, comprising skin and its associated structures, serves as the body's primary barrier against external factors.
- The circulatory system, including the heart, blood vessels, and blood, plays a critical role in transporting oxygen, nutrients, and waste products throughout the body.
- Understanding the cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying organ system function is crucial for the development of effective diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.
Introduction to Organ Systems

The human body is organized into 11 major organ systems, each with distinct functions and cellular compositions. These systems include the integumentary, skeletal, muscular, nervous, circulatory, lymphatic, respiratory, digestive, endocrine, urinary, and reproductive systems. The intricate relationships between these systems enable the body to maintain homeostasis, respond to external stimuli, and perform a wide range of physiological functions.
Cellular Composition of Organ Systems
Cells are the fundamental units of life, and their specialization and organization give rise to the diverse range of tissues and organs that comprise the human body. The cellular composition of each organ system is unique, reflecting the specific functions and requirements of that system. For example, the skin is composed of epithelial cells, which provide a barrier against external factors, while the nervous system is comprised of neurons and glial cells, which facilitate communication and coordination.
| Organ System | Primary Cell Types |
|---|---|
| Integumentary | Epithelial cells, melanocytes, fibroblasts |
| Skeletal | Osteoblasts, osteoclasts, osteocytes |
| Muscular | Skeletal muscle cells, smooth muscle cells, cardiac muscle cells |
| Nervous | Neurons, glial cells (astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia) |

Organ System Interdependencies

The various organ systems of the human body are intricately connected, and their functions are highly interdependent. For example, the circulatory system relies on the respiratory system to provide oxygen, while the nervous system relies on the circulatory system to deliver oxygen and nutrients to neurons. Understanding these interdependencies is essential for appreciating the complex dynamics of human physiology and for developing effective treatments for diseases and disorders.
Cell Signaling and Communication
Cells communicate with one another through a complex array of signaling pathways, which enable the coordination of physiological functions and responses to external stimuli. The mechanisms of cell signaling and communication are crucial for maintaining tissue and organ function, and their dysregulation can contribute to a range of diseases and disorders. By elucidating the molecular mechanisms underlying cell signaling and communication, researchers can develop novel therapeutic strategies for targeting specific cellular pathways.
In conclusion, the human body is a complex and fascinating entity, comprising various organ systems that work in tandem to maintain overall health and function. The cellular composition and function of each organ system are unique, reflecting the specific requirements and functions of that system. By understanding the intricate relationships between cells, tissues, and organs, researchers can develop more effective diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for a range of diseases and disorders.
What is the primary function of the integumentary system?
+The primary function of the integumentary system is to serve as a barrier against external factors, such as temperature, humidity, and pathogens, while also regulating body temperature and aiding in the production of vitamin D.
How do cells communicate with one another?
+Cells communicate with one another through a complex array of signaling pathways, which involve the release and reception of chemical signals, such as hormones and neurotransmitters.
What is the role of the circulatory system in maintaining overall health?
+The circulatory system plays a critical role in maintaining overall health by transporting oxygen, nutrients, and waste products throughout the body, while also regulating body temperature and aiding in the immune response.
Meta Description: Explore the intricate relationships between organ systems and cells, and discover how their functions and interdependencies maintain overall health and function in the human body. (149 characters)