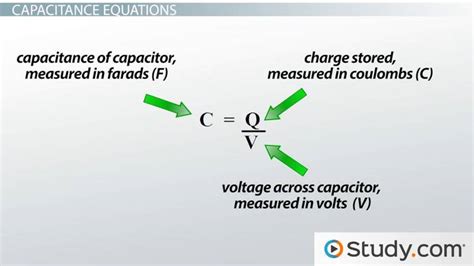
The equation for a capacitor is a fundamental concept in electrical engineering, describing the relationship between the charge stored on the capacitor, the voltage across it, and its capacitance. The capacitance of a capacitor is defined as the ratio of the charge stored on each plate to the potential difference between the plates. Mathematically, this is expressed as C = Q/V, where C is the capacitance, Q is the charge, and V is the voltage.
Capacitor Equation and Its Components

To delve deeper into the equation for a capacitor, it’s essential to understand the components involved. The capacitance © is measured in farads (F), charge (Q) is measured in coulombs ©, and voltage (V) is measured in volts (V). The equation C = Q/V implies that for a given voltage, the capacitance determines how much charge can be stored on the capacitor. This relationship is crucial in designing and analyzing electrical circuits.
Derivation of the Capacitor Equation
The derivation of the capacitor equation involves understanding the physical properties of capacitors. A capacitor consists of two conductive plates separated by a dielectric material. When a voltage is applied across the plates, electric field lines emanate from the positive plate and terminate on the negative plate. The capacitance is directly proportional to the area of the plates and inversely proportional to the distance between them, as given by the formula C = ε₀εᵣ(A/d), where ε₀ is the permittivity of free space, εᵣ is the relative permittivity of the dielectric material, A is the area of the plates, and d is the distance between them.
| Parameter | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|
| C | Farad (F) | Capacitance |
| Q | Coulomb (C) | Charge |
| V | Volt (V) | Voltage |
| ε₀ | F/m | Permittivity of free space |
| εᵣ | Unitless | Relative permittivity |
| A | m² | Area of the plates |
| d | m | Distance between the plates |

Applications of Capacitors and Their Equations
Capacitors find widespread applications in electronic circuits, including filtering, coupling, and energy storage. The equation for a capacitor is essential in designing these applications. For instance, in a simple RC circuit, the capacitor equation is used to determine the time constant (τ = RC), which dictates how the circuit responds to changes in voltage. This knowledge is crucial for engineers designing electronic devices, from simple audio filters to complex power supply systems.
Energy Stored in a Capacitor
The energy stored in a capacitor is another important aspect related to its equation. The energy (E) stored in a capacitor is given by the formula E = ½CV², where C is the capacitance and V is the voltage across the capacitor. This formula shows that the energy stored is directly proportional to the capacitance and the square of the voltage. This relationship is vital in applications where capacitors are used for energy storage, such as in power supplies and audio equipment.
Key Points
- The equation for a capacitor is C = Q/V, relating capacitance, charge, and voltage.
- Capacitance is influenced by the physical properties of the capacitor, including plate area and distance between plates.
- The energy stored in a capacitor is given by E = ½CV², showing a direct relationship with capacitance and the square of the voltage.
- Understanding the capacitor equation is crucial for designing and analyzing electronic circuits.
- Capacitors have diverse applications, including filtering, coupling, and energy storage, each relying on the principles described by the capacitor equation.
In conclusion, the equation for a capacitor is a foundational concept in electrical engineering, underpinning the design and analysis of a wide range of electronic circuits and devices. Its applications span from simple RC circuits to complex power systems, highlighting the importance of understanding the relationship between capacitance, charge, and voltage.
What is the primary function of a capacitor in an electronic circuit?
+A capacitor’s primary function is to store electrical energy in the form of an electric field. It can also be used for filtering, coupling, and other applications due to its ability to block DC voltage while allowing AC voltage to pass through.
How does the distance between the plates of a capacitor affect its capacitance?
+The capacitance of a capacitor is inversely proportional to the distance between its plates. Reducing the distance between the plates increases the capacitance, allowing the capacitor to store more charge for a given voltage.
What is the significance of the relative permittivity of the dielectric material in a capacitor?
+The relative permittivity (εᵣ) of the dielectric material affects the capacitance of the capacitor. A higher εᵣ value means the material is more effective at storing electric field lines, resulting in higher capacitance for the same physical dimensions.