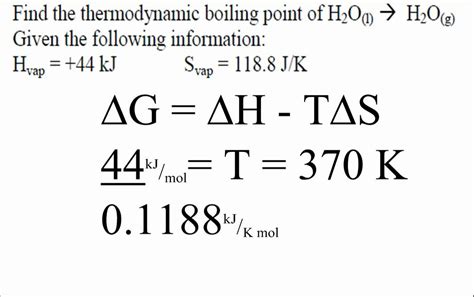
The Delta G equation, also known as the Gibbs free energy equation, is a fundamental concept in thermodynamics that helps predict the spontaneity of a chemical reaction. The equation is expressed as ΔG = ΔH - TΔS, where ΔG is the change in Gibbs free energy, ΔH is the change in enthalpy, T is the temperature in Kelvin, and ΔS is the change in entropy. This equation is crucial in understanding the thermodynamic feasibility of a reaction, as it takes into account both the energy changes (enthalpy) and the disorder or randomness (entropy) of the system.
Understanding the Components of the Delta G Equation

To fully appreciate the significance of the Delta G equation, it’s essential to understand its components. The change in enthalpy (ΔH) is a measure of the total energy change in a reaction, including the energy absorbed or released as heat. A negative ΔH indicates an exothermic reaction, where heat is released, while a positive ΔH indicates an endothermic reaction, where heat is absorbed. The change in entropy (ΔS) reflects the change in disorder or randomness of the system. A positive ΔS indicates an increase in disorder, which is favorable for spontaneity, while a negative ΔS indicates a decrease in disorder. The temperature (T) at which the reaction occurs is also a critical factor, as it influences the magnitude of the entropy term.
Interpreting the Delta G Equation
The sign and magnitude of ΔG determine the spontaneity of a reaction. A negative ΔG indicates a spontaneous reaction, meaning the reaction will proceed on its own under the given conditions. A positive ΔG indicates a non-spontaneous reaction, which requires energy input to proceed. A ΔG of zero indicates that the reaction is at equilibrium, with no net change in the concentrations of reactants and products. By analyzing the Delta G equation, chemists can predict whether a reaction is feasible under specific conditions and understand the factors that influence its spontaneity.
| Term | Description | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| ΔG | Change in Gibbs free energy | Joules (J) |
| ΔH | Change in enthalpy | Joules (J) |
| T | Temperature | Kelvin (K) |
| ΔS | Change in entropy | Joules per Kelvin (J/K) |

Key Points
- The Delta G equation (ΔG = ΔH - TΔS) is used to predict the spontaneity of a chemical reaction.
- A negative ΔG indicates a spontaneous reaction, while a positive ΔG indicates a non-spontaneous reaction.
- The change in enthalpy (ΔH) and the change in entropy (ΔS) are critical components of the Delta G equation.
- Temperature (T) influences the magnitude of the entropy term and the spontaneity of the reaction.
- Understanding the Delta G equation is essential for predicting the thermodynamic feasibility of a reaction and the factors that influence its spontaneity.
Applications of the Delta G Equation

The Delta G equation has numerous applications in chemistry and related fields. It is used to predict the spontaneity of reactions, understand the factors that influence reaction rates, and design new reactions with desired properties. In biochemistry, the Delta G equation is used to understand the energetics of metabolic pathways and the binding of molecules to enzymes or receptors. In materials science, the equation is used to predict the stability of materials and the feasibility of synthesis reactions.
Limitations and Considerations
While the Delta G equation is a powerful tool for predicting the spontaneity of reactions, it has limitations and considerations. The equation assumes that the reaction is at equilibrium, which may not always be the case. Additionally, the equation does not account for kinetic factors, such as reaction rates and catalysts, which can influence the spontaneity of a reaction. Furthermore, the equation requires accurate values for ΔH, ΔS, and T, which can be challenging to obtain experimentally or theoretically.
In conclusion, the Delta G equation is a fundamental concept in thermodynamics that helps predict the spontaneity of chemical reactions. By understanding the components of the equation and its applications, chemists can gain insights into the thermodynamic feasibility of reactions and the factors that influence their spontaneity. However, it is essential to consider the limitations and considerations of the equation, including the assumption of equilibrium and the neglect of kinetic factors.
What is the significance of the Delta G equation in predicting the spontaneity of a reaction?
+The Delta G equation is significant because it helps predict whether a reaction is spontaneous or non-spontaneous under given conditions. A negative ΔG indicates a spontaneous reaction, while a positive ΔG indicates a non-spontaneous reaction.
How does temperature influence the spontaneity of a reaction according to the Delta G equation?
+Temperature influences the magnitude of the entropy term (TΔS) in the Delta G equation. An increase in temperature can make a reaction more spontaneous by increasing the magnitude of the entropy term, while a decrease in temperature can make a reaction less spontaneous.
What are some limitations of the Delta G equation in predicting the spontaneity of a reaction?
+The Delta G equation assumes that the reaction is at equilibrium, which may not always be the case. Additionally, the equation does not account for kinetic factors, such as reaction rates and catalysts, which can influence the spontaneity of a reaction.